The Impact of COVID-19 on the U.S. Auto Industry
The numbers were horrendous but were drowned out in the cacophony of COVID-19 coronavirus news. Major domestic Chinese automakers and their joint ventures with foreign auto giants saw their February sales crater by as much as 92 percent. Now, with the virus spreading in the U.S., could the same thing happen here?
Understanding the Market Drop
To understand how the coronavirus could affect the U.S. auto industry, we must first note the staggering sales declines. For instance, Honda’s sales in China dropped by 85 percent, Toyota by 70 percent, and GM by 92 percent. These drops are primarily due to two key factors intertwined by a significant event: the Chinese government’s decision to impose lockdowns in areas like Hubei province, where around 60 million citizens were restricted from leaving their homes except to get groceries or seek medical attention. Consequently, this led to a dual crisis for the auto industry: potential customers could not purchase vehicles, and manufacturing plants were closed with no workforce available to build the cars.
Moreover, Hubei is not alone in its lockdown; at its peak, nearly four provinces and almost 50 cities throughout China faced similar restrictions, including key business hubs like Beijing and Shanghai.
Global Lockdowns: A Ripple Effect
The situation isn’t exclusive to China. For instance, Italy recently enacted nationwide lockdowns. This action has resulted in the largest domestic automaker, FCA, temporarily closing three plants that produce approximately 600,000 vehicles each year. Major players such as Lamborghini and Ferrari indicated they would also be closing facilities or reducing output in response to the crisis. These closures are significant when considering their impact on both local economies and global car supply.
The Risk of U.S. Lockdowns
America may experience similar lockdowns if the outbreak escalates. New Rochelle in New York has already implemented a lockdown. Severe outbreaks in Washington State and California’s Santa Clara County have led to drastic precautionary measures, such as the closure of entertainment venues and public spaces in major cities like Los Angeles.
The auto industry has swiftly canceled major events, including auto shows in Geneva and New York, which has financial ramifications for manufacturers who invest millions in preparations. Such cancellations not only prevent instant revenue generation but also diminish interest in future vehicle sales.
The Response from Major Automakers
In response to increasing health concerns, companies like Ford, GM, and FCA have asked employees to work from home. While there have been no reports of widespread factory closures, an employee at an FCA plant tested positive for the virus, prompting one facility to pause operations. The potential for similar disruptions exposes a vulnerability in the U.S. auto manufacturing sector, which plays a crucial role in the national economy, contributing around 4.3% to the GDP.
If production is affected by outbreaks, it can lead to immediate consequences within communities. The ripple effect of a parts supplier’s closure—especially when many components are sourced from China—can halt assembly lines dependent on those parts. Automakers have stated that they currently have sufficient inventory, but many anticipate that future supply challenges could develop.

Furthermore, manufacturing plants in Mexico are also facing challenges sourcing parts from China, running the risk of shutdowns. While some German automakers assert they are not experiencing supply chain issues, both Japanese and Korean manufacturers have reported disruptions.
Changing Consumer Behavior
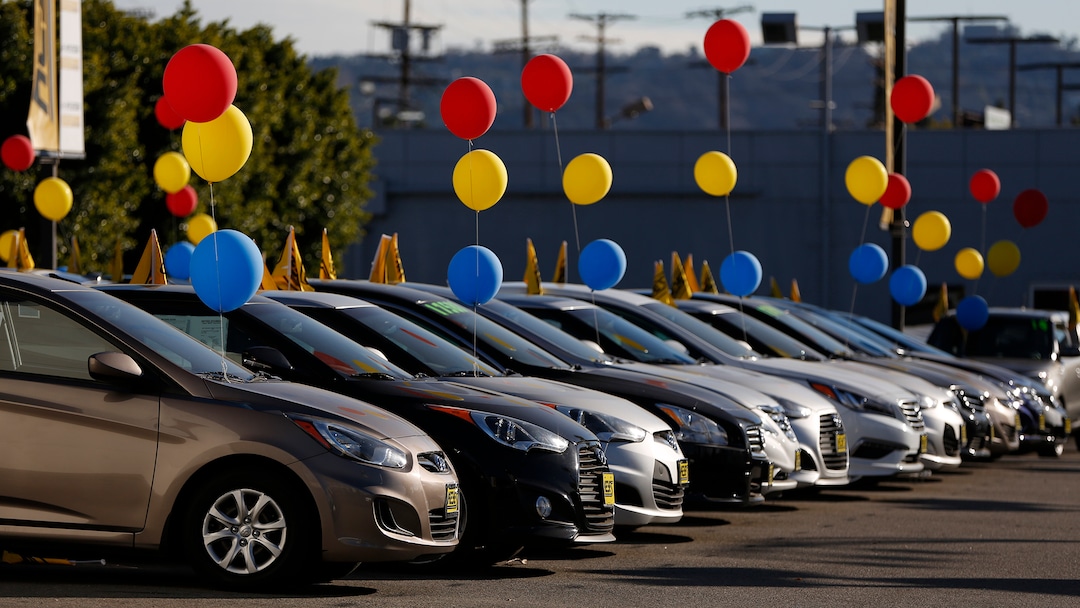
However, the potential ramifications extend beyond manufacturing to consumer behavior. Individual outbreaks and measures like large gathering bans are causing apprehension among potential buyers, leading to decreased foot traffic at dealerships. Even in areas where the virus has not yet made a significant impact, people are hesitant to visit public spaces, which affects vehicle sales.
Economic uncertainty exacerbates this trend. With the automotive industry representing a major financial commitment for individuals, many prospective buyers may delay purchases as they prioritize savings over significant expenditures during these unpredictable times. If widespread job losses or serious economic downturns occur, the consequences for car sales could be severe.
Future Projections
While the exact impact of these factors remains unclear, analysts suggest a potential nine-percent reduction in car sales for 2020. Early reports indicated sales could drop from 17.1 million in 2019 to 15.5 million in 2020 due to economic uncertainty affecting consumer confidence.
The true extent of this downturn will likely become more evident as North American plants experience potential shortages in Chinese-sourced parts. Furthermore, the first quarter sales figures, expected in April, should provide a clearer picture of the impacts following a strong February performance. Nevertheless, if consumers continue to avoid showrooms due to health and financial concerns, auto sales may remain suppressed.
In summary, while there are many uncertainties regarding the duration of this crisis, the ramifications for the automotive industry are profound, and ongoing developments will need to be closely monitored.